Meta Description: Wondering about carbide end mill lifespan? This guide breaks down the factors affecting tool life, from material to machining parameters, and provides expert tips to maximize it.
Introduction
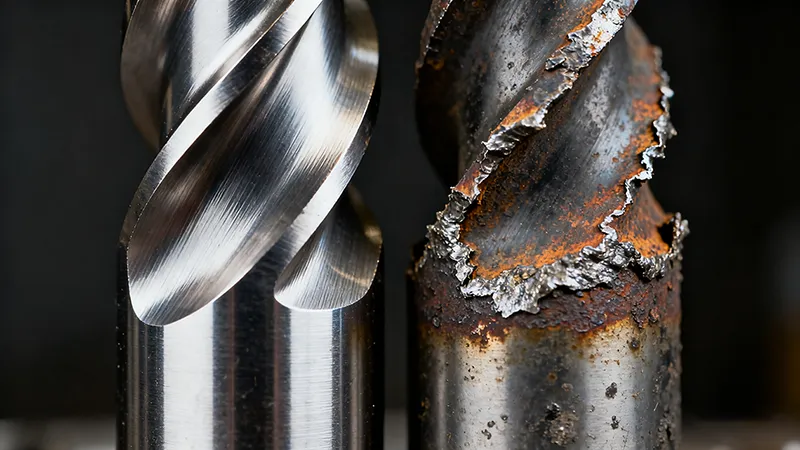
Carbide end mills are indispensable tools in CNC machining, renowned for their ability to efficiently cut metals, composites, and plastics. A common question among machinists and workshop managers is: “What is their actual lifespan?” The answer is complex, as it depends on a interplay of factors including workpiece material, cutting parameters, tool quality, and maintenance. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of carbide end mill longevity, supported by authoritative data and practical tips to help you extend tool life and reduce costs.
1. Understanding Carbide End Mills
Carbide end mills, also known as solid carbide tools, are primarily made from tungsten carbide (WC) particles bonded with a cobalt (Co) binder. This composition gives them superior hardness and wear resistance compared to high-speed steel (HTS) tools, making them ideal for high-speed and high-precision applications.
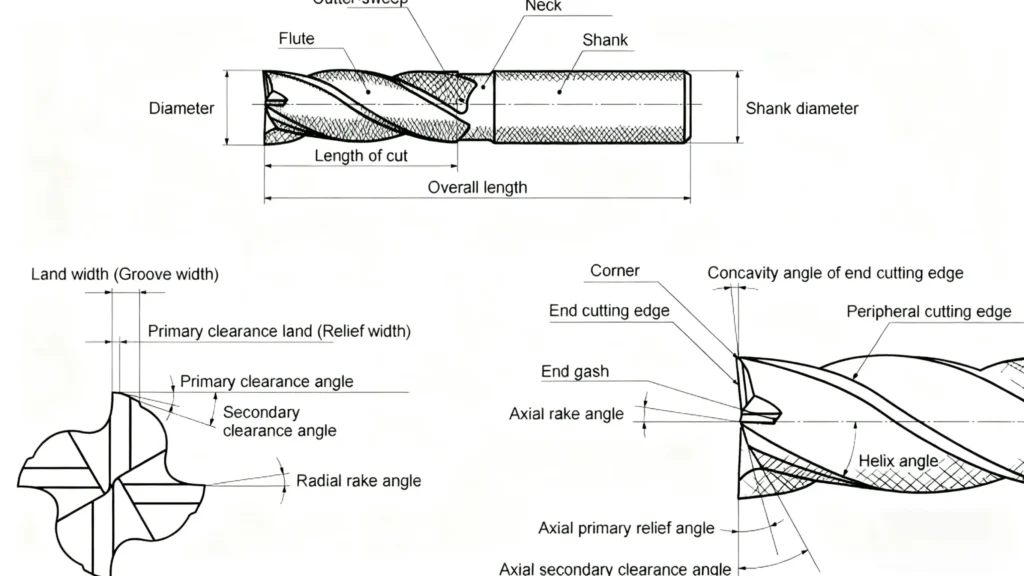
2. Key Factors Affecting Carbide End Mill Lifespan
A. Workpiece Material
The material being machined is the most significant factor. Harder and more abrasive materials drastically accelerate tool wear.
- Aluminum: 50–100 hours of life is achievable under optimal conditions.
- Mild Steel: Typical life ranges from 10 to 30 hours.
- Stainless Steel & Titanium: These tough materials can reduce lifespan to under 10 hours due to high cutting forces and work hardening.
B. Cutting Parameters (Speed, Feed, Depth of Cut)
Improper parameters are a leading cause of premature tool failure.
- Speed & Feed: Running an end mill too fast generates excessive heat, while running it too slow can cause rubbing and edge buildup. Use professional calculators like the GWizard Speeds and Feeds Calculator or, even better, consult the cutting data provided by your tool manufacturer, such as Kennametal’s milling calculator or Mitsubishi Materials’ Speed & Feed calculator.
- Depth of Cut (DOC): Using a step-over (radial DOC) of less than the tool’s diameter and a reasonable axial DOC reduces load and heat, significantly extending life.
C. Tool Coating
Modern coatings like TiN (Titanium Nitride), TiAlN (Titanium Aluminum Nitride), and AlCrN (Aluminum Chromium Nitride) provide a hard, thermally resistant layer that reduces friction and dissipates heat.
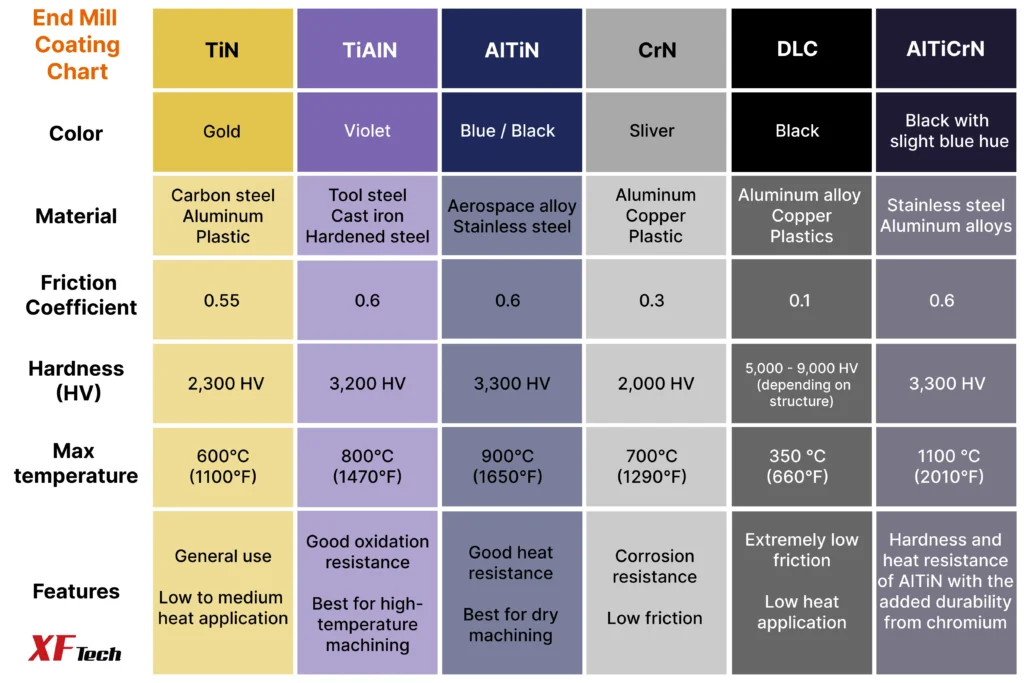
According to research in surface engineering, advanced coatings can increase tool life by over 200%, as demonstrated in technical reports from coating specialists. Choosing the right coating is critical; a comprehensive guide like this one from Harvey Performance Company can be very helpful.
D. Cooling and Lubrication
Effective use of coolant or mist lubrication is critical. It carries away heat, reduces friction, and helps flush chips away. Dry machining, especially in ferrous metals, can easily cut tool life in half due to thermal shock and adhesion.
3. Typical Lifespan Ranges and When to Replace Your Tool
A general lifespan for a carbide end mill can range from 10 to 100 hours of actual cutting time. The key is to monitor for signs of wear and replace the tool before it fails catastrophically.
Signs of a Worn End Mill:
- Flank Wear: A uniform wear land on the tool’s clearance face. Replace the tool if it exceeds 0.3 mm for finishing or 0.5 mm for roughing.
- Chipping or Fracture: Visible nicks or breaks along the cutting edge.
- Poor Surface Finish: Increased roughness, burrs, or tearing on the machined part.
- Unusual Noises or Vibration: A change in the sound of the cut often indicates a dull tool.
For a standardized definition of tool life evaluation, refer to the ISO 8688-1:1989 Standard for Tool life testing in milling – Part 1: Face milling. This international standard provides the scientific methodology for determining and comparing tool life.
4. Practical Tips to Extend End Mill Life
- Optimize Speeds and Feeds: Never guess your parameters. Use reliable reference data from manufacturers like Sandvik Coromant’s CoroPlus® ToolGuide or ISCAR’s SUMO POWER Calculators.
- Ensure Tool Rigidity: Use the shortest tool possible and a high-quality collet to minimize vibration and runout. Resources like REGO-FIX’s technical guides on toolholding explain the importance of rigidity in detail.
- Apply the Right Coating: Match the coating to your material. For example, use TiAlN for high-temperature alloys and uncoated or polished tools for aluminum.
- Implement Proper Chip Evacuation: Ensure chips are being effectively cleared from the cut to prevent re-cutting, which accelerates wear.
- Inspect and Maintain Regularly: Clean and inspect tools after use. Store them in a dry, organized environment.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can a carbide end mill be re-sharpened?
Yes, carbide end mills can be re-sharpened by a specialized regrinding service. However, this process may alter the original geometry and is not always cost-effective for standard tools. It’s best suited for expensive, custom tools.
Q2: How should I store my end mills?
Store them individually in a dry, climate-controlled environment to prevent corrosion. Use original packaging or a dedicated tool organizer to prevent physical damage.
Q3: How does carbide compare to High-Speed Steel (HSS)?
Carbide end mills typically last 3 to 5 times longer than HSS tools when machining hard materials and can run at much higher speeds. However, they are more brittle and prone to chipping under improper conditions or intermittent cuts. A detailed comparison can be found in guides provided by suppliers like MSC Industrial Supply’s “Carbide vs HSS” resource.
Conclusion
The lifespan of a carbide end mill is not a fixed number but a variable that you can actively influence. By understanding the key factors of material, parameters, coating, and cooling, you can make informed decisions that maximize tool life, improve part quality, and boost overall productivity. Investing in high-quality tools and adhering to best practices is the most effective strategy for long-term cost savings.
For further technical specifications and standards, consult resources from leading engineering organizations like the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) Digital Collection which contains a wealth of research papers on machining and tooling.


